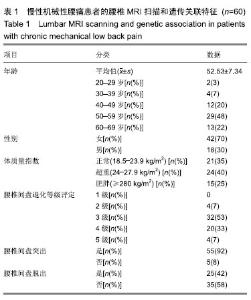
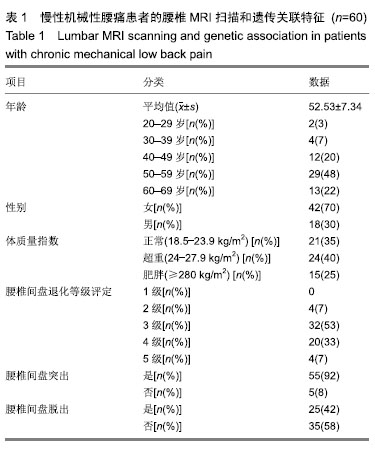
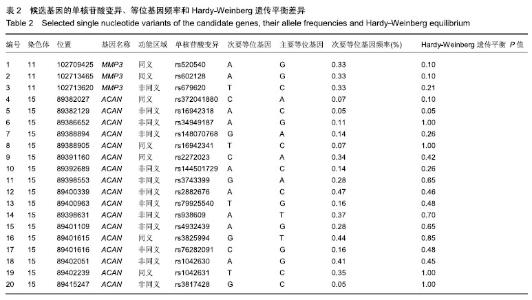
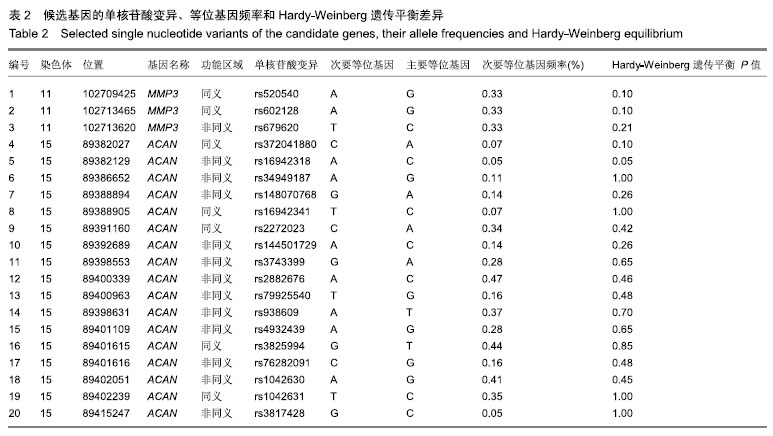
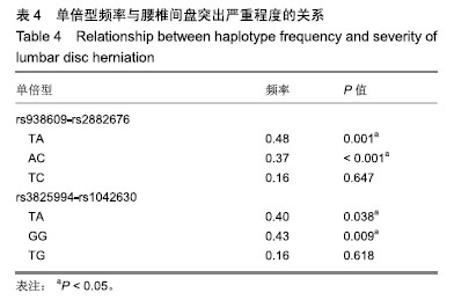
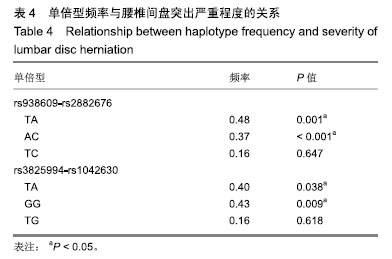
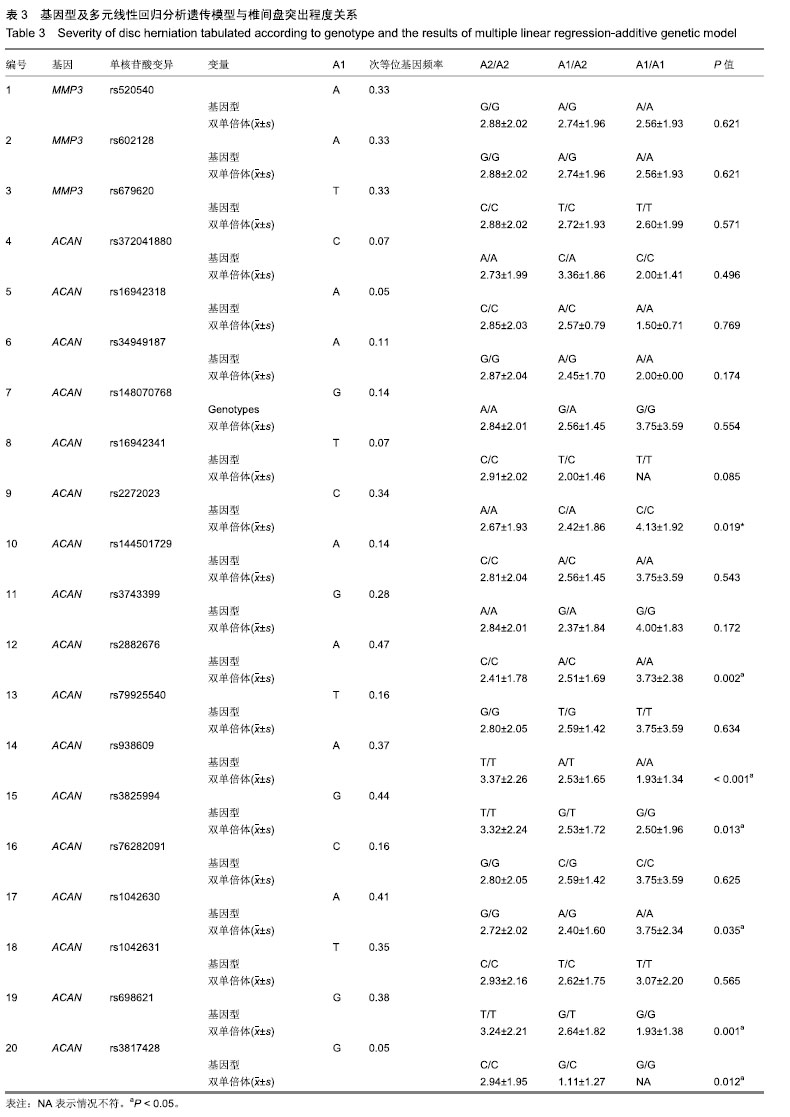
| [1]马信龙.腰椎间盘突出症的病理学分型及其临床意义[J].实用骨科杂志, 2016,22(4):384.[2]Perera RS, Dissanayake PH, Senarath U, et al. Single Nucleotide Variants of Candidate Genes in Aggrecan Metabolic Pathway Are Associated with Lumbar Disc Degeneration and Modic Changes. PLoS One. 2017;12(1):e0169835. [3]高克海,李洪涛,黄彩虹.聚集蛋白聚糖酶-1在退变椎间盘中的表达及意义[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(15):1412-1416.[4]耿翔,吕国华.聚集蛋白聚糖基因多态性与腰椎间盘退变相关性的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(4):370-372.[5]Cong L, Zhu Y, Pang H, et al. The interaction between aggrecan gene VNTR polymorphism and obesity in predicting incident symptomatic lumbar disc herniation. Connect Tissue Res. 2014;55(5-6):384-390. [6]李峰,廖泉森,杨新海.MMP3与腰椎间盘突出症间盘突出程度的相关性研究[J].新疆医学,2010,40(2):43-46.[7]丛琳,朱悦,屠冠军.聚集蛋白聚糖基因串联重复多态性与腰椎间盘突出症相关性研究[J].中华外科杂志,2015,53(2):116-120.[8]蒋家耀,卢旭华. 椎间盘退变生物学治疗的研究进展[J].中国骨伤, 2016, 29(6):576-580.[9]王毅翔,吴爱悯,Santiago FR.腰痛患者如何选择影像学检查的循证医学依据[J].重庆医学,2018,47(18):2389-2398.[10]Omair A, Holden M, Lie BA, et al. Treatment outcome of chronic low back pain and radiographic lumbar disc degeneration are associated with inflammatory and matrix degrading gene variants: a prospective genetic association study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14:105. [11]李国强.基于医学指标与体质量指数关系评价肥胖标准的方法[J].中国组织工程研究,2007,11(43):8745-8748.[12]Lane NE, Nevitt MC, Genant HK, et al. Reliability of new indices of radiographic osteoarthritis of the hand and hip and lumbar disc degeneration. J Rheumatol. 1993;20(11):1911-1918.[13]王蓉,杜永浩,杨健,等.腰椎间盘退变MRI分级系统的一致性评价[J].实用放射学杂志,2016,32(11):1740-1744.[14]杨占辉,孙建华,丁浩.腰椎间盘突出症的评分法疗效评定标准[J].颈腰痛杂志,1999(1):20-21.[15]孙博.非同义突变对蛋白质翻译后修饰的影响及其在人类疾病中的意义[D].上海:上海交通大学,2015.[16]Katsonis P, Koire A, Wilson SJ, et al. Single nucleotide variations: biological impact and theoretical interpretation. Protein Sci. 2014; 23(12):1650-1666. [17]耿翔.人聚蛋白聚糖基因多态性与腰椎间盘退变性疾病的相关性[D].长沙:中南大学,2013.[18]薛静波,王文军,晏怡果,等.骨保护素基因多态性与椎间盘退变的相关性研究[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志, 2016,8(6):352-358.[19]Huang X, Chen F, Zhao J, et al. Interleukin 6 (IL-6) and IL-10 Promoter Region Polymorphisms Are Associated with Risk of Lumbar Disc Herniation in a Northern Chinese Han Population. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2017;21(1):17-23. [20]Eser B, Eser O, Yuksel Y, et al. Effects of MMP-1 and MMP-3 gene polymorphisms on gene expression and protein level in lumbar disc herniation. Genet Mol Res. 2016;15(3). [21]路康,杨匡,李海音,等.髓核细胞来源外泌体对骨髓间充质干细胞向髓核样细胞分化的作用[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2016,26(10):933-938.[22]Videman T, Saarela J, Kaprio J, et al. Associations of 25 structural, degradative, and inflammatory candidate genes with lumbar disc desiccation, bulging, and height narrowing. Arthritis Rheum. 2009; 60(2):470-481. [23]Smith LJ, Nerurkar NL, Choi KS, et al. Degeneration and regeneration of the intervertebral disc: lessons from development. Dis Model Mech. 2011;4(1):31-41.[24]Kepler CK, Anderson DG, Tannoury C, et al. Intervertebral disk degeneration and emerging biologic treatments. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011;19(9):543-553.[25]谭平先,李健,孙筱放,等.聚集蛋白聚糖基因多态性与腰椎间盘突出症的关联性[J].中国组织工程研究,2011,15(33):6257-6261.[26]肖飞,刘国辉.椎间盘退变的遗传学机制研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2007,15(21):1632-1634. |